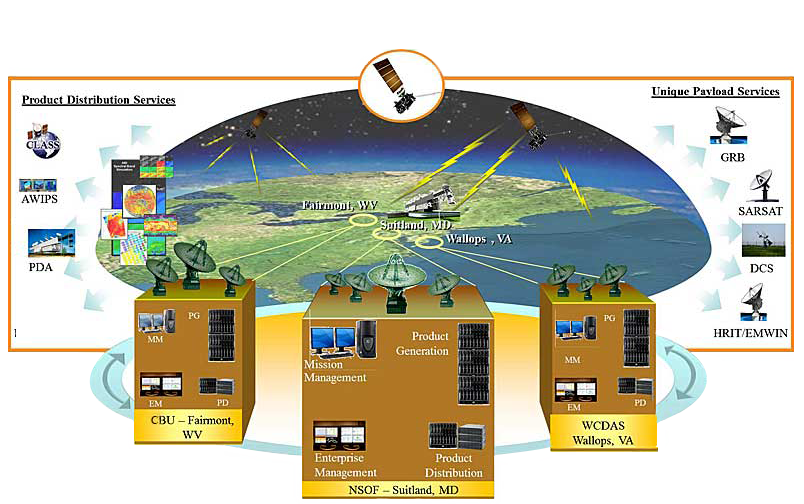
User Systems: Overview
Product Distribution and Unique Payload Services
Click for details
GOES Rebroadcast (GRB) is the primary space relay of level 1b products and replaces the GOES VARiable (GVAR) service. GRB provides full resolution, calibrated, navigated, near-real-time direct broadcast data. These data are available to all users with GRB receivers in view of a GOES-R Series satellite at the east or west operational longitudes.
Additional GRB informationThe Advanced Weather Interactive Processing System (AWIPS) is an interactive computer system that integrates meteorological and hydrological data, enabling forecasters to prepare forecasts and issue warnings.
- The National Weather Service (NWS) is the primary operational user of GOES-R Series data and receives key data directly from the GOES-R/AWIPS interface.
- The National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) and the National Weather Center Telecommunications Gateway (NWSTG) receives Level 1b, 2, and 2+ data directly from the AWIPS distribution sever.
The Environmental Satellite Processing and Distribution System (ESPDS) system is responsible for receiving and storing real-time environmental satellite data and products and making them available to authorized users. The Product Distribution and Access (PDA) provides real-time distribution and access services for GOES-R Series users.
Additional PDA informationThe Comprehensive Large Array-data Stewardship System is a web-based data archive and distribution system for NOAA’s environmental data. CLASS provides retrospective data access and distribution services of GOES-R data to all users.
Scientists, researchers, and academics interested in viewing archived environmental products (older than 7 days) including satellite data from GOES-R Series satellites can acquire the data through CLASS.
- CLASS provides a long term data storage facility in which environmental data can be permanently stored.
- CLASS stores Level 0, Level 1b, and Level 2+ data.
- CLASS provides user access to archived data for GOES-R Series satellites in addition to POES, DMSP, and other GOES data.
- CLASS serves as the single location within NOAA from which users can receive all archived environmental data.
- CLASS data is formatted for NetCDF visualization.
The Data Collection System (DCS) is a relay system used to collect information from a large number of Earth-based platforms that transmit in-situ environment sensor data on predefined frequencies and schedules, in response to thresholds in sensed conditions, or in response to interrogation signals. In the GOES-R era, the number of user-platform channels expanded from 266 to 433. There was also a frequency change from 1696 MHz to 1679 MHz, which required replacement of users’ Low Noise Block (LNB) feed. Data transmission rates in the GOES-R era are 300 bps and 1200 bps.
Additional DCS informationThe Emergency Managers Weather Information Network (EMWIN) is a direct service that provides users with weather forecasts, warnings, graphics, and other information directly from the National Weather Service (NWS) in near real time. The GOES EMWIN relay service is one of a suite of methods to obtain these data and display the products on the user’s personal computer. The High Rate Information Transmission (HRIT) service provides broadcast of low-resolution GOES satellite imagery data and selected products to remotely located user HRIT Terminals.
Additional HRIT/EMWIN informationAs an integral part of the international search and rescue satellite program called COSPAS-SARSAT, NOAA operates the Search and Rescue Satellite Aided Tracking (SARSAT) System to detect and locate mariners, aviators, and other recreational users in distress almost anywhere in the world at any time and in almost any condition. This system uses a network of satellites to quickly detect and locate distress signals from emergency beacons onboard aircraft, vessels, and from handheld personal locator beacons called PLBs. The SARSAT transponder carried onboard GOES-R Series satellites provides the capability to immediately detect distress signals from emergency beacons and relay them to ground stations - called Local User Terminals. In turn, this signal is routed to a SARSAT Mission Control Center and then sent to a Rescue Coordination Center that dispatches a search and rescue team to the location of the distress.
The GOES-R Series continues the legacy Geostationary SAR (GEOSAR) function of the SARSAT system onboard NOAA’s GOES satellites which has contributed to the rescue of thousands of individuals in distress. The SARSAT transponder was modified slightly for the GOES-R Series to operate with a lower uplink power (32 dBm), enabling the satellites to detect weaker signal beacons.
For more information about SARSAT, visit the NOAA SARSAT web site and the NASA SAR Mission Office web site.
The range of the user community is reflected in the wide variety and applications of GOES-R Series data and products.
Larger, institutional users can exploit the increases in spectral, temporal, and spatial resolution and assimilate radiances for use in prediction models, increasing the timeliness and accuracy of forecast products.GOES-R Series data is used in real time for critical life and property forecasting and warning applications primarily by the National Weather Service. These users can monitor the rapid development and interaction of severe storms
Smaller public and private sector users obtain GOES-R Series data through their own Earth stations, or through terrestrial network distribution.
Data Access
GOES-R Series data products are available using new product distribution and access technologies. The graphic below illustrates the GOES-R Series system architecture showing product distribution and Unique Payload Services that are detailed from the links in the upper right of this page.